Home › Forums › Oral Diagnosis & Medicine › EPULIS FISSURATUM
Welcome Dear Guest
To create a new topic please register on the forums. For help contact : discussdentistry@hotmail.com
- This topic has 5 replies, 3 voices, and was last updated 03/01/2012 at 8:36 pm by
Anonymous.
-
AuthorPosts
-
03/01/2012 at 4:44 pm #10244
 drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times
drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 timesEpulis fissuratum (also known as “Granuloma fissuratum”[1]:808) is an oral pathologic condition that appears in the mouth as an overgrowth of fibrousconnective tissue. Also referred to less commonly as inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia, denture epulis, and denture induced fibrous hyperplasia, it is associated with the edges of a denture that does not fit well. The word, “epulis”, can be used to describe any gingival tumor, but it is widely used in association with this specific condition
Causes
Epulis fissuratum appears as a single or multiple fold of tissue that grown in excess around the alveolar vestibule, which is the area where the gums meet the inner cheek. Usually, the edge of the denture rests in between two of the folds. The excess tissue is firm and fibrous, and ulcerations may be present. The size of the affected tissue varies widely, since almost the entire length of tissue around a denture can be affected. More commonly found in women, it can appear in either the mandible or maxilla (upper jaw) but is more commonly found in the anterior portions of the mouth rather than in the posterior. Women during pregnancy can also present with an epulis, which will resolve after birth. Fibroepithelial polyps, pedunculated lesions of the palate beneath an upper denture, are associated with this condition. An epulis fissuratum in a patient without dentures can also be diagnostic of Crohn’s disease.
The appearance of an epulis fissuratum microscopically is an overgrowth of cells from the fibrous connective tissue. The epithelial cells are usually hyperkeratotic and irregular, hyperplastic rete ridges are often seen.Epulis fissuratum can also appear around dental implants. In this photo, taken after antibiotic and periodontal therapy, it occurred because the implant denture clasp had broken and the patient exhibited poor oral hygiene.
03/01/2012 at 4:46 pm #15025 drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times
drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 timesEpulis fissuratum arises in association with denture flanges. Consequently, epulis fissuratum is usually observed in the maxillary or mandibular vestibule.
Mortality/Morbidity
Significant morbidity does not occur with epulis fissuratum.
Race
Most cases of epulis fissuratum are observed in whites. This, no doubt, relates to the predominance of whites as denture wearers.
Sex
Most studies indicate a clear predilection for epulis fissuratum in females.[2]The fact that women are more likely than men to wear their dentures for prolonged periods because of their reluctance to be seen without them probably plays a significant role. In addition, more women than men wear dentures and are more likely to seek treatment. Possibly, atrophic epithelial changes secondary to menopause may influence an increased reaction to trauma in older females.
Age
Epulis fissuratum occurs in greatest numbers in the fifth, sixth, and seventh decades, but it can be observed at almost any age. Epulis fissuratum has been described in children. The fact that the lesions are related to denture wear and chronicity of an irritative process explains the higher incidence in older individuals.
-
Examination of an epulis fissuratum patient typically reveals folds of hyperplastic mucosa, which encompass the border of the denture flange. The edge of the denture usually fits in a groove between the folds. The lesions are most frequently observed at the facial aspect of the denture. The occurrence of this on the lingual surface is unusual. They are more often observed in the anterior portion of the jaws; however, a predilection for the maxilla or the mandible does not seem to exist.
-
The surface of the epulis fissuratum mass tends to be smooth; however, occasionally, it is ulcerated (most often within the depth of the groove) or papillary.
-
The size of the epulis fissuratum lesion is variable; some lesions are small, but they can be extensive and involve the entire length of the vestibule.[5]
-
Although frequently of normal mucosal color, erythema may be associated with inflammation. Some lesions have a more pyogenic granuloma –like appearance because of capillary proliferation.
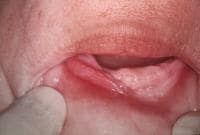 An epulis fissuratum in the anterior part of the mandible shows a central groove where the denture flange rests. Note the inflammatory erythema. The surface of the lesion is usually smooth as shown in the image.
An epulis fissuratum in the anterior part of the mandible shows a central groove where the denture flange rests. Note the inflammatory erythema. The surface of the lesion is usually smooth as shown in the image.
03/01/2012 at 4:49 pm #15026Drsumitra
OfflineRegistered On: 06/10/2011Topics: 238Replies: 542Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 timesSurgically excise the epulis fissuratum because even removal of the offending stimulus (ie, denture) will not result in complete resolution. In addition, correct the denture; otherwise, the lesion will recur. Either make a new denture or reline the old denture. The use of laser therapy is discussed in recent studies
Regular dental care can prevent epulis fissuratum. Patients who wear dentures frequently believe that they no longer require care, and, under these circumstances, dentures lose their correct fit and become the source of irritation.With correction of the poorly fitting denture, the prognosis for epulis fissuratum is excellent.
Instruct the patient that regular dental care is necessary and that the oral tissues are changing constantly. This means that dentures are not permanent and need adjustments over time
03/01/2012 at 4:51 pm #15027Drsumitra
OfflineRegistered On: 06/10/2011Topics: 238Replies: 542Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times03/01/2012 at 8:34 pm #15028Anonymous
03/01/2012 at 8:36 pm #15029Anonymous
Histologic Findings
Epulis fissuratum is a hyperplastic reactive lesion, often with inflammatory and reparative phases. The histologic picture can be variable. Most frequently, a dense fibrous hyperplasia occurs, often with varying degrees of inflammation and vascularity. Because capillary proliferation is considerable, an overlap with pyogenic granuloma occurs. Mucous glands are often present in the specimen and may show a chronic sialadenitis. Occasionally, the glands may have an associated lymphoid hyperplasia and papillary ductal hyperplasia. The epithelium may be atrophic or hyperplastic and occasionally shows a pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. Ulceration can occur. Infrequently, chondroid or osseous metaplasia can develop within the mass.
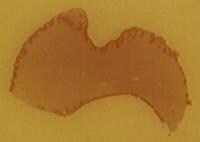 A view of a whole mount of a tissue section taken from an epulis fissuratum shows that it is essentially a fibrous hyperplasia. The central groove can be observed, and, in this patient, papillary hyperplasia is present in some areas.
A view of a whole mount of a tissue section taken from an epulis fissuratum shows that it is essentially a fibrous hyperplasia. The central groove can be observed, and, in this patient, papillary hyperplasia is present in some areas. -
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.