Home › Forums › Periodontology › EROSION OF TEETH DUE TO GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
Welcome Dear Guest
To create a new topic please register on the forums. For help contact : discussdentistry@hotmail.com
- This topic has 4 replies, 1 voice, and was last updated 17/03/2012 at 5:09 pm by
 drmithila.
drmithila.
-
AuthorPosts
-
17/03/2012 at 4:58 pm #10393
 drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times
drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 timesTooth surface loss increases for people with gastroesophageal reflux disease, according to a new study.
The information appears in the Journal of the American Dental Association.
The University of Tennessee Health Science Center put this study together to analyze the tooth surface loss for patients with GERD. At the beginning of the study and after six months, dental impressions were taken of 12 people with GERD and the results were compared to six people without the disease. The results were then digitized, and divided into categories based on the degree of tooth surface loss.
The mean volume loss per tooth was much greater among the patients with GERD. In fact the loss per tooth was 0.18 mm3 compared to 0.06 mm3 for patients without GERD.
Based on this study, people with some kind of acid reflux issues need to pay close attention to the impact the problem has on their teeth. Many people need to be more educated about the serious damage that acid regurgitation may cause to one’s teeth
17/03/2012 at 4:58 pm #15293 drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times17/03/2012 at 5:07 pm #15294
drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times17/03/2012 at 5:07 pm #15294 drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times
drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 timesTooth erosion affects the whole surface of the tooth. If the problem is not identified and treated early enough, the damage to tooth structures may be so extensive that it requires expensive cosmetic dentistry to restore function and appearance.
 The treatment of dental erosion includes two separate steps. The first step is the identification and elimination of the reasons that have caused the tooth erosion and the second step is to treat the symptoms and to restore tooth enamel loss with restorative procedures by a cosmetic dentist.
The treatment of dental erosion includes two separate steps. The first step is the identification and elimination of the reasons that have caused the tooth erosion and the second step is to treat the symptoms and to restore tooth enamel loss with restorative procedures by a cosmetic dentist.A. Eliminate the causes
of tooth erosionDiet. If the cause of the dental erosion is the consumption of acidic foods or drinks, patient education may solve the problem. The patient must make dietary modifications as those described in the next section about the prevention of tooth erosion.
Medical consultation. If the problem is caused by medical condition as GERD the patient must consult a medical doctor for the appropriate treatment. In case of bulimia caused tooth erosion a psychologist may help to treat the condition.
B. Restore tooth enamel lossTreatment of dental erosion depends on the severity of the damage. If the loss of tooth enamel is moderate without affecting the patient’s appearance, there is no need of restorative treatment. The dentist may recommend certain fluoride treatments and de-sensitizing toothpastes to control the tooth sensitivity symptoms caused by teeth erosion. Enhancing the re-mineralization process by providing minerals such as fluoride may be enough for natural tooth enamel restoration. The dentist may also apply a fluoride varnish on the affected teeth for further protection and repair of tooth enamel.
Restorative cosmetic treatments become necessary if the tooth enamel damage is extensive. Depending on the degree of tooth wear, restorative treatment can range from placement of bonded composites (tooth bonding) in a few isolated areas of teeth erosion, to crowns, dental porcelain veneers, bridges or even full mouth reconstruction in the case of severe tooth enamel damage. A cosmetic dentist has to evaluate the situation and recommend the best cosmetic treatment to restore teeth function and appearance.
Regardless of the type of treatment required, the patient who has suffered dental erosion must follow a careful preventive plan to avoid further tooth enamel loss and the high expenses of the associated cosmetic treatments.
Regular preventive dental visits are very important for the prevention of tooth erosion. During the dental exam, the dental hygienist can easily identify early signs of erosion before it causes significant damage to teeth.
You should always check carefully before you choose a dental insurance if preventive dental visits and ‘cosmetic’ restorative procedures are covered.
Prevention of dental erosion and tooth enamel lossTooth erosion can do severe damage to your teeth, but it is preventable. There are several preventive measures that can be taken to control tooth enamel loss and prevent dental erosion:
Decrease the consumption of acidic foods and/or drinks, both in quantity and frequency. Try to have them only at mealtimes. Replace carbonated drinks with water, milk or un-sweetened coffee and tea, especially between meals.
Drink acidic drinks quickly and do not swish them round the mouth (to reduce the time that the teeth are exposed to acids).
Use a straw when drinking carbonated beverages or fruit juices, which are very acidic (at least to limit contact of acids with the front teeth).
After eating or drinking acidic foods or beverages, rinse your mouth with fresh water so that the acid is diluted and easier neutralized.
Because acids temporarily soften the tooth surface (de-mineralization), don’t brush your teeth immediately after eating or drinking something acidic (or vomiting), as the softened enamel will be further damaged by the brushing and that will speed up the process of erosion. Wait at least an hour to allow calcium in saliva to repair tooth enamel after the acid exposure.
Chewing sugar-free gum can help reduce dry mouth and increase the saliva flow, allowing it to neutralise acids and help teeth to remineralize.17/03/2012 at 5:08 pm #15295 drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times
drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 timesDental erosion (tooth erosion) is the irreversible loss of tooth enamel due to chemical processes that do not involve bacterial action.
Tooth enamel is a mineralized hard tissue that covers and protects the tooth. It is the hardest tissue of human body but it can be chemically dissolved in an acidic environment. The acids that cause dental erosion may come from intrinsic (e.g., gastroesophageal reflux, vomiting) or extrinsic sources (e.g., acidic beverages, citrus fruits).The tooth enamel loss caused by the acids produced by dental plaque bacteria (tooth decay) is not dental erosion. Other forms of tooth enamel loss caused by mechanical and not chemical factors are tooth abrasion and tooth attrition.
Tooth erosion is a slow progressive process that leads to the loss of the protective hard tissues of the tooth caused by exposure to acids for long periods of time.
Modern life-style and dietary habits are responsible for a sharp increase in the prevalence of dental erosion, especially in the young population of developed countries. Teeth erosion is becoming increasingly common and can have long-term consequences for the patient’s dental health.
Dental erosion can cause mild tooth problems, such as tooth discoloration and mild sensitivity, to more severe dental problems, such as indentions in the teeth, severe tooth sensitivity, cracked teeth and tooth loss.17/03/2012 at 5:09 pm #15296 drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 times
drmithila
OfflineRegistered On: 14/05/2011Topics: 242Replies: 578Has thanked: 0 timesBeen thanked: 0 timesDe & Re-mineralization of tooth enamel
If the tooth is exposed to acidic environment, the tooth enamel starts to loose minerals in a process called de-mineralization. Saliva slowly neutralises the acidity in the mouth and restores it to its natural balance. When the tooth’s environment becomes non-acidic the reverse process of re-mineralization begins. This natural tooth enamel restoration process repairs the enamel using minerals such as calcium from saliva and fluoride from toothpastes. If the two processes are balanced any damage to the tooth enamel is totally repaired.
Unfortunately there are many factors that disturb this delicate balance in favor of the de-mineralization resulting in irreversible tooth enamel loss. In the case of dental erosion, the problem occurs from the fact that the increased intensity and frequency of acid attacks does not allow enough time to repair and restore tooth enamel through re-mineralization.
Causes of tooth erosionTooth erosion generally occurs as a result of the chemical action of acids on the tooth surfaces. These acids that can be either extrinsic or intrinsic dissolve gradually the tooth enamel from the surface of the tooth.
Causes of tooth erosion due to extrinsic acids (from outside the body):
Frequent consumption of acidic foods and drinks is the main cause of tooth enamel loss.
o Even though fruit juices and fresh fruits are considered as healthy foods, their over-consumption is not the best option for teeth because they are too acidic (very low pH). Most of the popular carbonated drinks, soft drinks, sports drinks and diet drinks are also very acidic. Even fizzy mineral water can be acidic. Common extrinsic dietary acids include citric acid, phosphoric acid, ascorbic acid, malic acid and carbonic acid.
o The erosive potential of acidic drinks does not depend on pH alone. Also, factors such as frequency and method of intake of acidic beverages as well as proximity of tooth brushing after intake may influence susceptibility to teeth erosion. Drinking through a straw lessens the contact time of the acids with the teeth. On the contrary, swishing the drink around the teeth increases their exposure to acids.
Some medicines are acidic and, therefore, erosive. They can cause dental erosion on direct contact with the teeth when the medication is chewed or held in the mouth prior to swallowing.
Environmental factors such as the chlorine and other chemicals in swimming pools can cause erosion over time.
Causes of tooth erosion due to intrinsic acids (from inside the body):
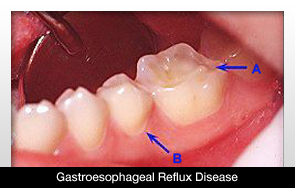
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or acid reflux, in which stomach acids come up into the oesophagus and mouth, can cause severe tooth erosion. Gastric acids are highly acidic with pH levels that can be less than 1.
Eating disorders that cause frequent vomiting are also responsible for tooth enamel loss caused by the gastric acids.
Bulimia (anorexia nervosa) is another frequent cause of eroded teeth due to chronic excessive vomiting. Besides vomiting, persons who suffer from bulimia tend to consume larger quantities of fresh fruits and acidic beverages that worsen the problem.
Alcoholism could also cause vomiting related loss of tooth enamel.
Low salivary flow rate is a significant risk factor for dental erosion due to reduced pH buffering capacity (its ability to neutralize changes in mouth’s pH)
Signs and Symptoms of Tooth ErosionTeeth erosion affects the whole surface of the teeth, unlike tooth abrasion and attrition where the symptoms are isolated in specific areas of the tooth.
Most of the symptoms of dental erosion are caused by the decreased depth of the tooth enamel layer that covers the crown of the tooth.
Early Symptoms of Tooth Erosion
Teeth Discoloration – Since the dentin of the tooth is exposed during tooth erosion, discoloration or yellowing of the teeth can occur. The more dentin that is exposed, the more yellow the teeth will become.
Tooth Sensitivity – Sensitive teeth are very common symptoms of teeth erosion because the enamel that protects the teeth wears away, leaving exposed the dentin (the softer, sensitive part of the tooth).
Rounded/Shorter Teeth – Teeth with dental erosion have usually a rounded look. If the tooth enamel loss is extensive teeth might also look shorter.
Transparency – The tips of the front teeth might look transparent.
Advanced Symptoms of Tooth Erosion
Cracking – If tooth erosion continues, the edges of the teeth can start to crack and have a rough feeling.
Pulp exposure in deciduous teeth
Tooth decay – teeth affected by dental erosion are more likely to suffer from tooth decay. -
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.