Home › Forums › Oral Diagnosis & Medicine › EPULIS FISSURATUM › EPULIS FISSURATUM
Epulis fissuratum arises in association with denture flanges. Consequently, epulis fissuratum is usually observed in the maxillary or mandibular vestibule.
Mortality/Morbidity
Significant morbidity does not occur with epulis fissuratum.
Race
Most cases of epulis fissuratum are observed in whites. This, no doubt, relates to the predominance of whites as denture wearers.
Sex
Most studies indicate a clear predilection for epulis fissuratum in females.[2]The fact that women are more likely than men to wear their dentures for prolonged periods because of their reluctance to be seen without them probably plays a significant role. In addition, more women than men wear dentures and are more likely to seek treatment. Possibly, atrophic epithelial changes secondary to menopause may influence an increased reaction to trauma in older females.
Age
Epulis fissuratum occurs in greatest numbers in the fifth, sixth, and seventh decades, but it can be observed at almost any age. Epulis fissuratum has been described in children. The fact that the lesions are related to denture wear and chronicity of an irritative process explains the higher incidence in older individuals.
-
Examination of an epulis fissuratum patient typically reveals folds of hyperplastic mucosa, which encompass the border of the denture flange. The edge of the denture usually fits in a groove between the folds. The lesions are most frequently observed at the facial aspect of the denture. The occurrence of this on the lingual surface is unusual. They are more often observed in the anterior portion of the jaws; however, a predilection for the maxilla or the mandible does not seem to exist.
-
The surface of the epulis fissuratum mass tends to be smooth; however, occasionally, it is ulcerated (most often within the depth of the groove) or papillary.
-
The size of the epulis fissuratum lesion is variable; some lesions are small, but they can be extensive and involve the entire length of the vestibule.[5]
-
Although frequently of normal mucosal color, erythema may be associated with inflammation. Some lesions have a more pyogenic granuloma –like appearance because of capillary proliferation.
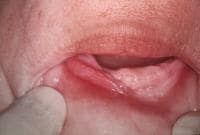 An epulis fissuratum in the anterior part of the mandible shows a central groove where the denture flange rests. Note the inflammatory erythema. The surface of the lesion is usually smooth as shown in the image.
An epulis fissuratum in the anterior part of the mandible shows a central groove where the denture flange rests. Note the inflammatory erythema. The surface of the lesion is usually smooth as shown in the image.